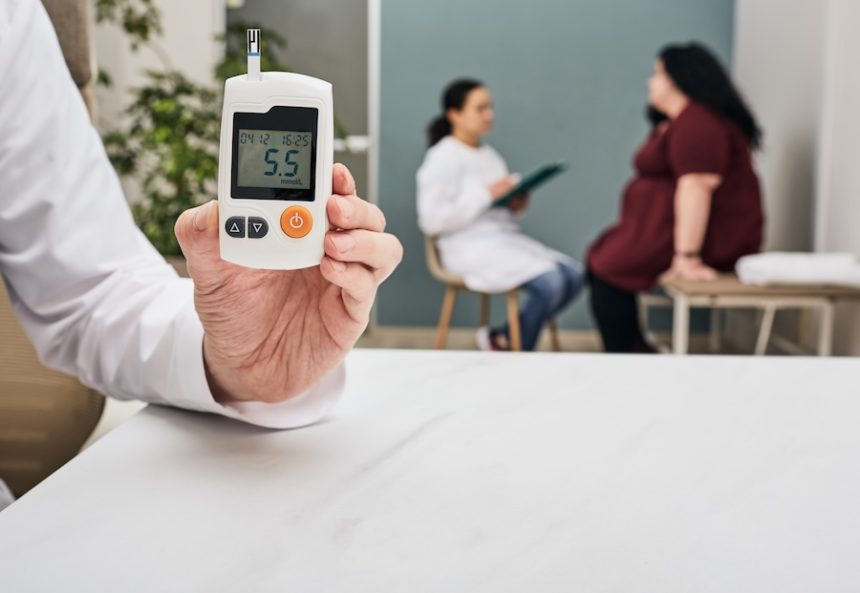
Two tests that are frequently used in the management and diagnosis of diabetes are the A1c test and the fasting glucose test. Although both are essential instruments for measuring blood sugar, their functions and applications differ. It can be easier to monitor and manage diabetes if you know when to use each test.
What is a fasting glucose test?
After a person has gone at least eight hours without eating, a fasting glucose test determines the amount of glucose in their blood. Usually, this test is used to identify prediabetes or diabetes. It gives an instantaneous picture of blood glucose levels, which is especially helpful when detecting hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) or hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) in a controlled environment.
When is a fasting glucose test appropriate?
Fasting glucose testing are especially useful in three circumstances:
- Initial Screening: The fasting glucose test is used as an initial screening tool for diabetes, especially in individuals with risk factors such as obesity, family history of diabetes, or symptoms of high blood sugar.
- Monitoring: It can be used to monitor glucose levels in individuals already diagnosed with diabetes to ensure their management plan is effective.
- Pre-surgical Assessments: Sometimes fasting glucose tests are required before surgery to ensure blood sugar levels are stable.
What is an A1c Test?
The A1c test calculates the average blood sugar levels over the previous two to three months. It is sometimes referred to as the hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test. It accomplishes this by determining the proportion of glycated or sugar-coated hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells.
When is an A1c Test appropriate?
The following situations are where an A1c test is most frequently used:
- Long-term Monitoring: Ideal for monitoring long-term glucose control in individuals with diabetes. It provides a broader view of how well blood sugar levels are being managed over time.
- Diagnosis: An A1c Test can be used to diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes.
- Adjusting Treatment Plans: This test can help doctors adjust diabetes treatment plans by providing insights into how well the current management strategies are working.
What are the key differences with the tests?
- Time Frame: Fasting glucose provides a snapshot of current blood sugar levels, while A1c offers an average of blood sugar levels over several months.
- Preparation: Fasting glucose requires fasting, whereas A1c does not require any special preparation.
- Usage: Fasting glucose is often used for immediate assessment, while A1c is used for long-term monitoring and management.
With their distinct perspectives on blood sugar levels, the A1c and fasting glucose tests are both crucial for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes. People and healthcare professionals can better manage and monitor diabetes and eventually improve health outcomes by knowing the distinctions and appropriate situations for each test.
East Idaho is where Kirk Bigley was raised. Prior to becoming a PA, he spent eight years in the US Navy. After his return to Idaho, he is pleased to work at East Idaho Community Care Westside, where he treats patients of all ages. Community Care is open from 7 a.m. to 7:30 p.m., Monday through Saturday, and from 10 a.m. to 6 p.m. on Sundays. Walk-ins are welcome; call (208) 525-2600 to make an appointment.